Clinical Translation of MRgHIFU
Clinical Translation of MRgHIFU
Minimally invasive ablation of liver tumorsProject Info
Start date:
September 2024
End date:
August 2028
Funding:
Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF)
Coordinator:
HUG – Division of Radiology

Summary
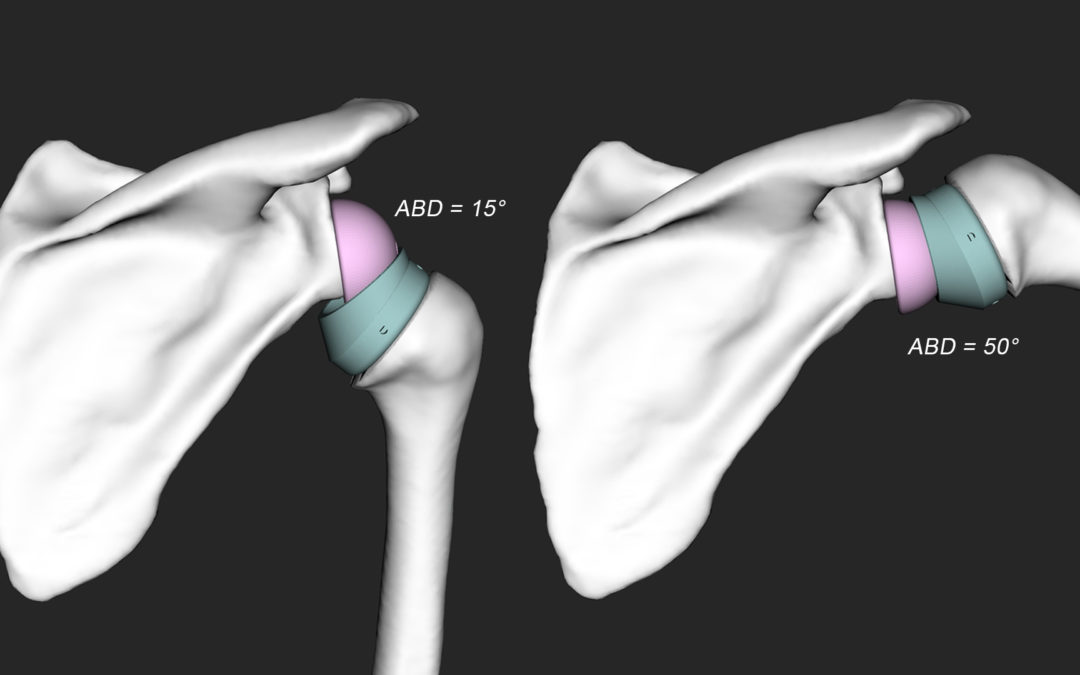
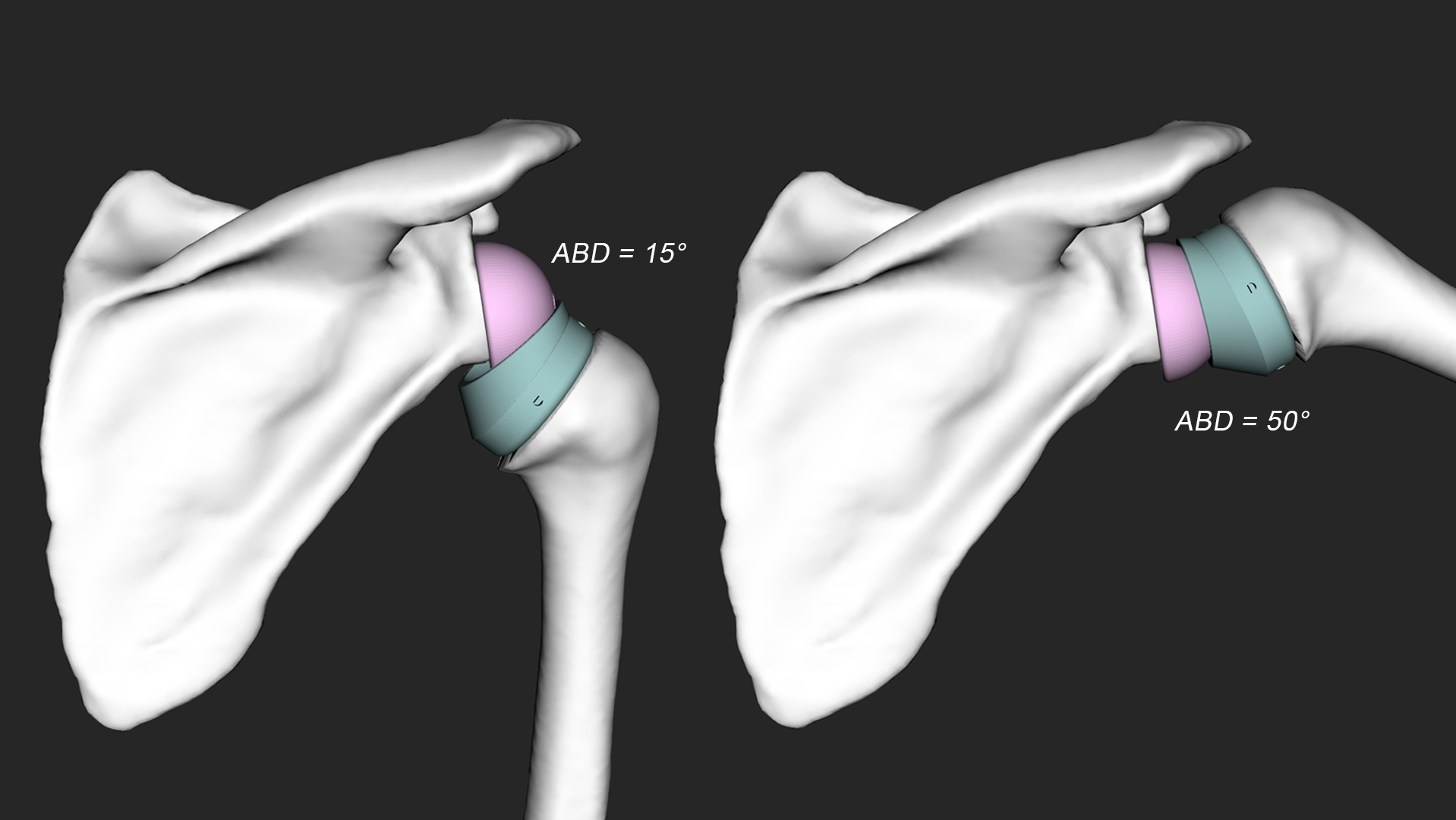
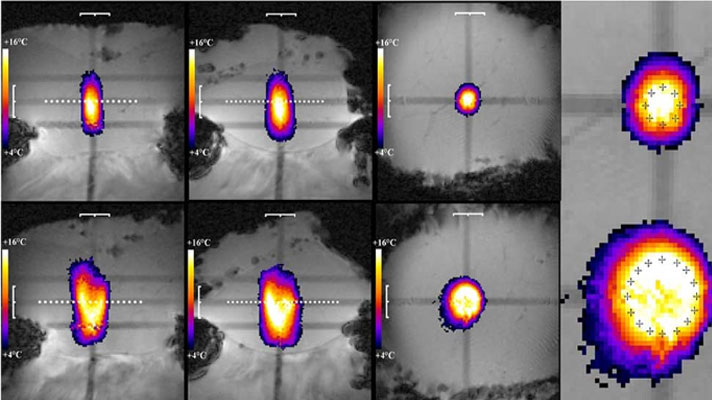
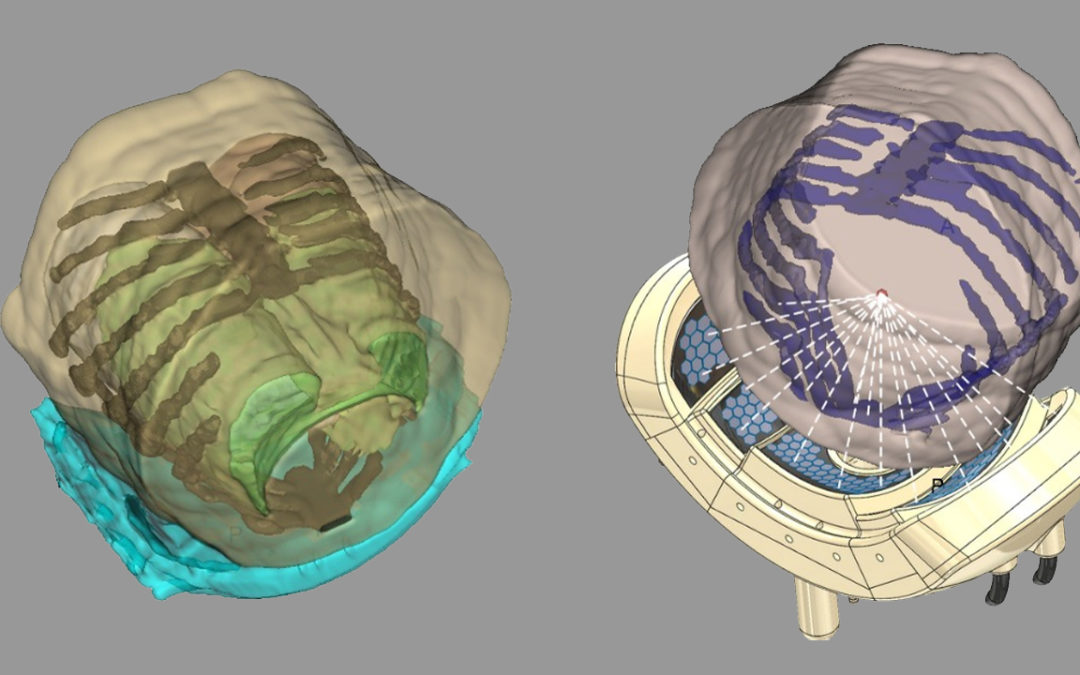
High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is a precise method to thermally ablate deep-seated tumors in a non-invasive manner. A prerequisite for a safe and effective application of HIFU is image guidance, to plan and control the ablation process. The most suitable imaging modality is MRI, with its high soft tissue contrast and its ability to monitor tissue temperature changes (MR-guided HIFU, MRgHIFU). The therapy of abdominal organs, such as the liver, still poses several problems due to a moving target location caused by breathing, motion related MR-thermometry artefacts and near-field obstacles, i.e. thoracic cage or bowel.
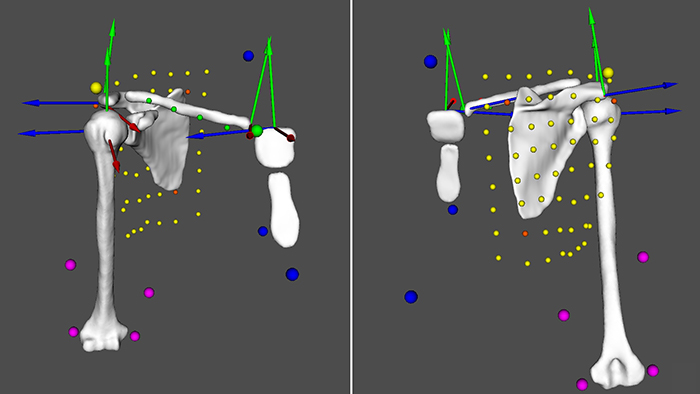
The primary objective of this project is to perform clinical trials with MRgHIFU applied to liver neoplastic nodules. The project relies on a new concept of MRgHIFU ultrasound developed in a previous SNF project which will be tested for the first time on patients. The clinical studies will meet incremental requirements in liver from basic targeting to complete tumour ablation.
In this project, Artanim is the expert in computer science, involving the design, implementation, and quality assurance of real time software for integration of “self-scanning” sonication with closed loop temperature feedback control.
Partners
University Hospitals of Geneva – Division of Radiology
Imaging, data analysis, transducer development, clinical tests and project coordination
University Hospitals of Geneva – Division of Oncology
Clinical trials
University Hospitals of Geneva – Department of Surgery
Liver surgery
Artanim
Design, implementation and quality assurance of real time software for integration of “self-scanning” sonification