MoRehab XR
MoRehab XR
Motion tracked rehabilitation through extended realitiesProject Info
Start date:
August 2020
End date:
December 2026
Funding:
–
Coordinator:
Artanim
Summary
After a stabilization surgery or a traumatic accident, physical rehabilitation is often required to restore the joint’s normal function. This process requires very regular and repetitive training sessions. The regularity and involvement of the patient being critical for success of the procedure, maintaining them interested and motivated while repeating similar exercises over and over is one of the main challenges of the physical therapist. During these sessions, it is also difficult to objectively monitor small progresses or the lack of the latter. On the other end of the spectrum, some video games have proved to be very effective in motivating people to perform pretty repetitive tasks on their controllers in order to travel through a story or a challenge.
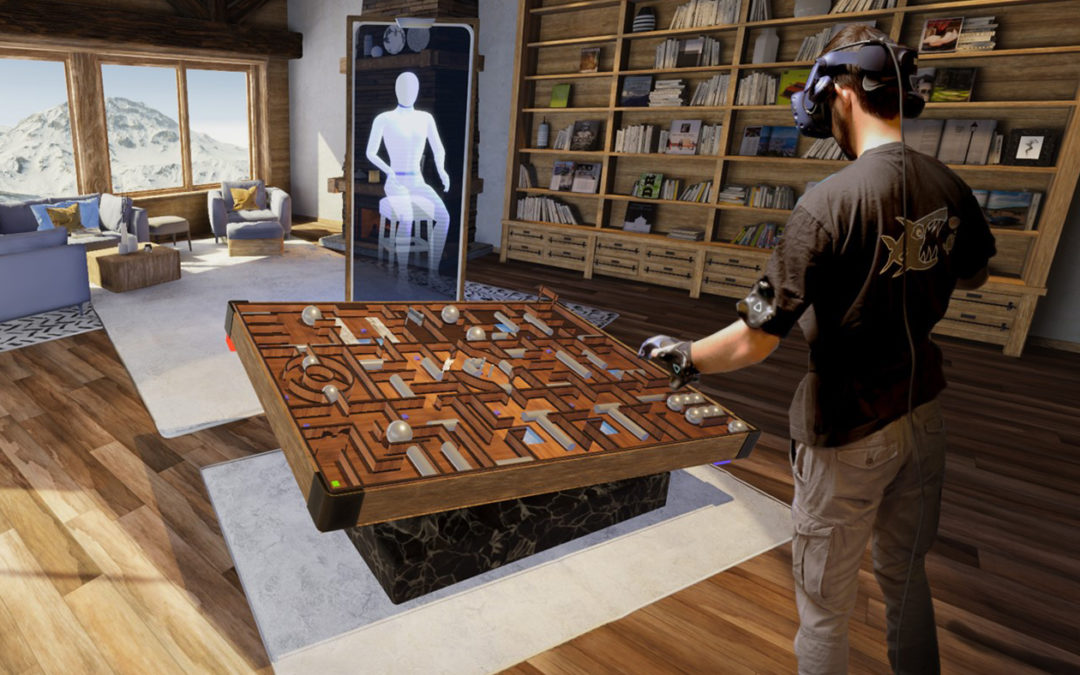
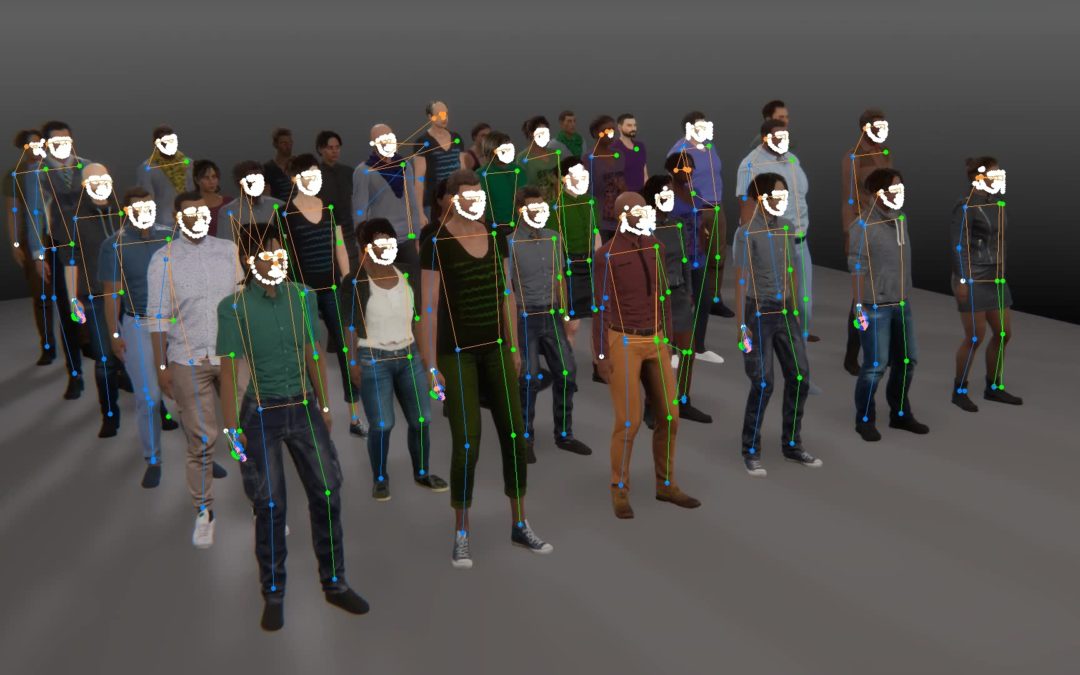
The goal of this project is to use the captivating capabilities of video games to entertain and motivate the patients through their rehabilitation, by designing a set of “exercise games” (called exergames) that will be won by performing the correct routines required for a proper physical rehabilitation. Through the use of modern motion tracking technology, the exergames will also be able to track the evolution of the physical recovery of the patients on a session per session basis, to adapt the challenges that the patients will face based on their needs and actual capacities, and if need be to alert the medical personnel early if some problems persist, or if no progresses are observed.
In this project, Artanim is in charge of building a platform suitable for these exergames, as well as designing and developing these exergames, and implementing the tools for a standard assessment of the patient’s performance. On the other hand, the medical usability and validity of the setup and exergames will be tested and assessed by the clinical team of La Tour Hospital over a large set of voluntary patients. Both teams will also work together to develop metrics to evaluate and adapt the patient’s performance during the sessions, thanks to the extended capabilities of the motion tracking system with respect to the data available in conventional physical therapy.
Partners
Artanim
Conception of the exergames and of a platform adapted to perform them, development of a set of medical scores adapted to the extended capabilities of the motion tracking system
La Tour Hospital – Division of Orthopedic and Trauma Surgery
Clinical tests, co-design of new physical evaluation metrics adapted to the motion tracking capabilities
Related Publications
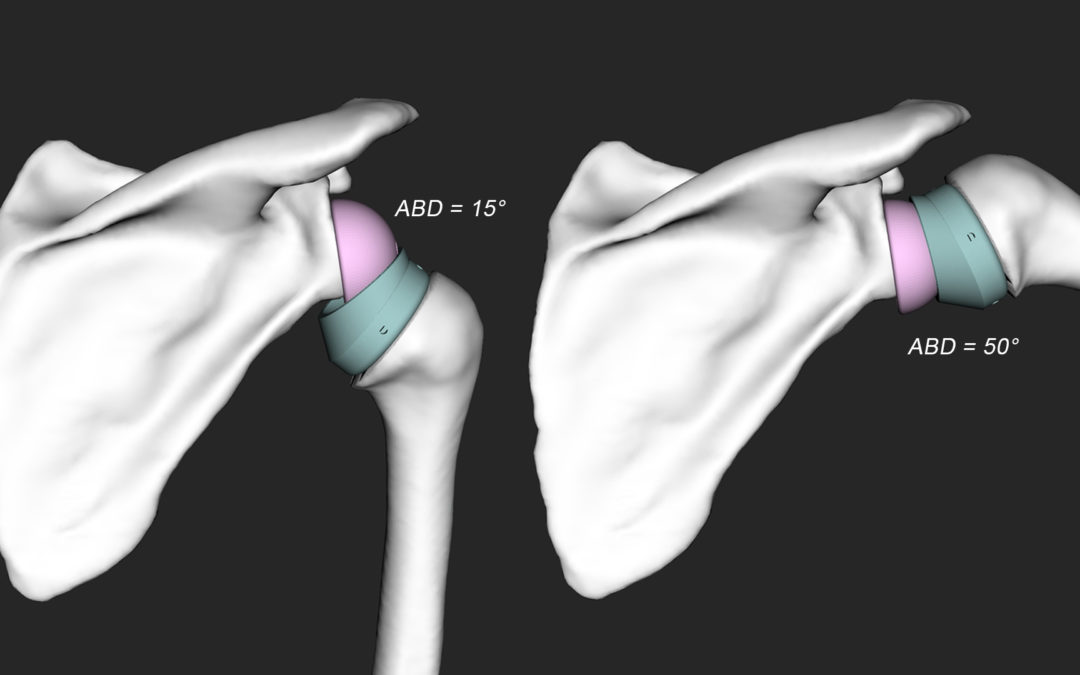
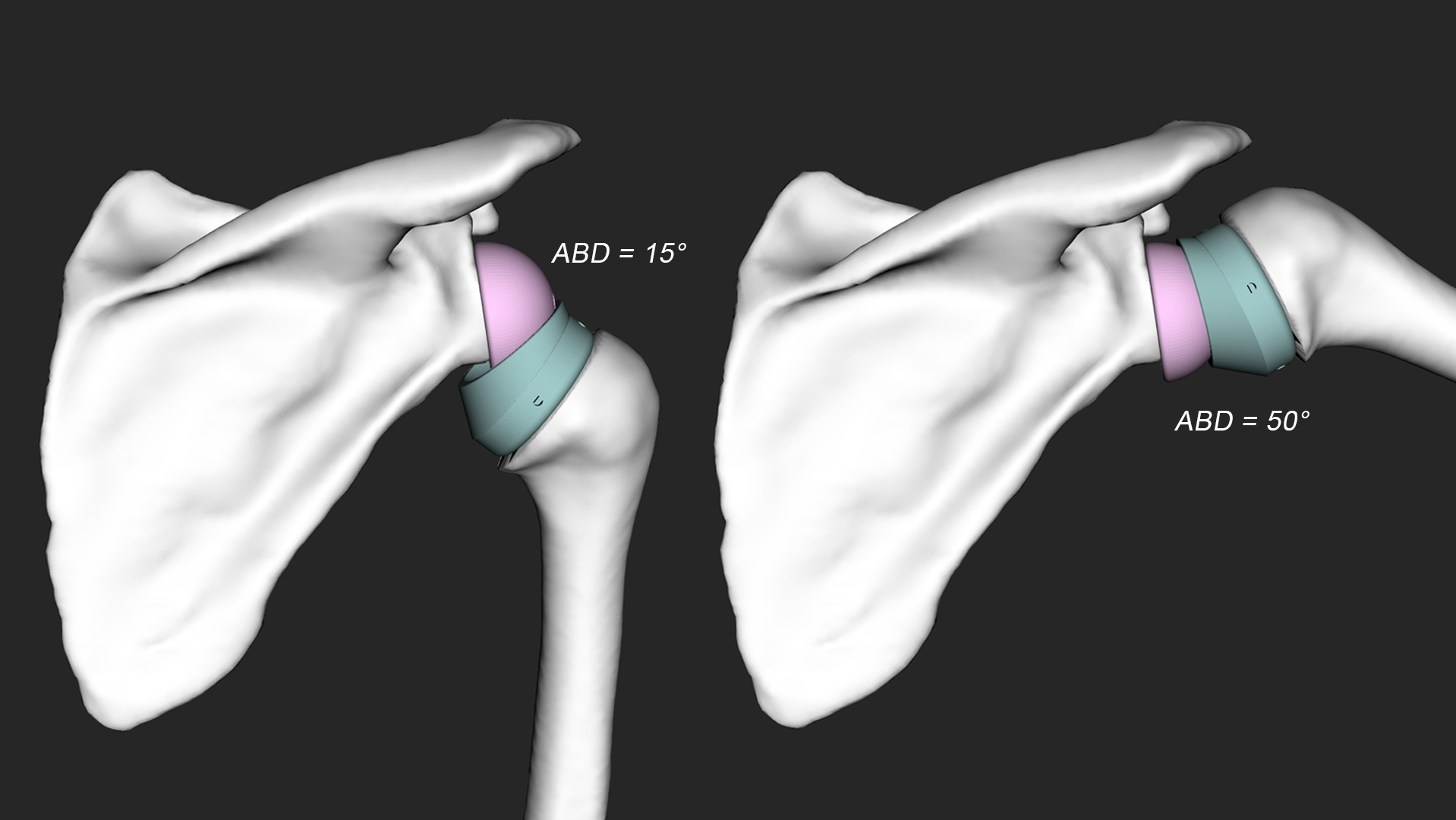
Mancuso M, Charbonnier C. Technical evaluation of the fidelity of the HTC Vive for upper limb tracking, 42nd International Conference on Biomechanics in Sports, Salzburg, Austria, July 2024.
PDF